2024.07.26
CTI Engineering Co., Ltd. developed a road structure knowledge system (AI tool for similar case search based on image/text information).
Technology & Research
For the purpose of assisting on-site inspectors with the assessment of damage during regular bridge inspections to achieve improved efficiency and sophistication of inspection tasks, CTI Engineering developed an AI tool that searches for and outputs cases similar to the damage image captured on site from a massive database of past regular bridge inspection information (image and text information).
1. Background
After the ceiling board fall accident that occurred in the Chuo Expressway Sasago Tunnel in 2012, regular close-up visual bridge inspections (once in five years) have been mandated since 2014, which is drastically increasing the time and cost spent on inspections up to this date.
The damage assessment (Level A to E) as per the Guidelines for Periodic Road Structure Inspections (hereinafter, "Inspection Guidelines") established by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism ("MLIT") requires technical understanding and decision, which gives cause for concern for variations in decisions among technicians. Such concern is calling for new technologies that improve inspection efficiency or help the determination of the degree of damage.
While many studies and products that apply AI technologies to inspection images have been reported, none has yet succeeded in determining the degree of damage according to the Inspection Guidelines.
2. Technology overview and features
In response to the pre-existing situation, we developed an AI tool that searches for and outputs similar cases from a massive database of regular bridge inspection information (image and text information of different types of damage of each part). As an input data, the tool uses on-site images captured during past regular bridge inspections and accompanying information, such as parts and types of damage (specifications), that are provided in the National Road Infrastructure Inspection Database published by the MLIT are used as input data.
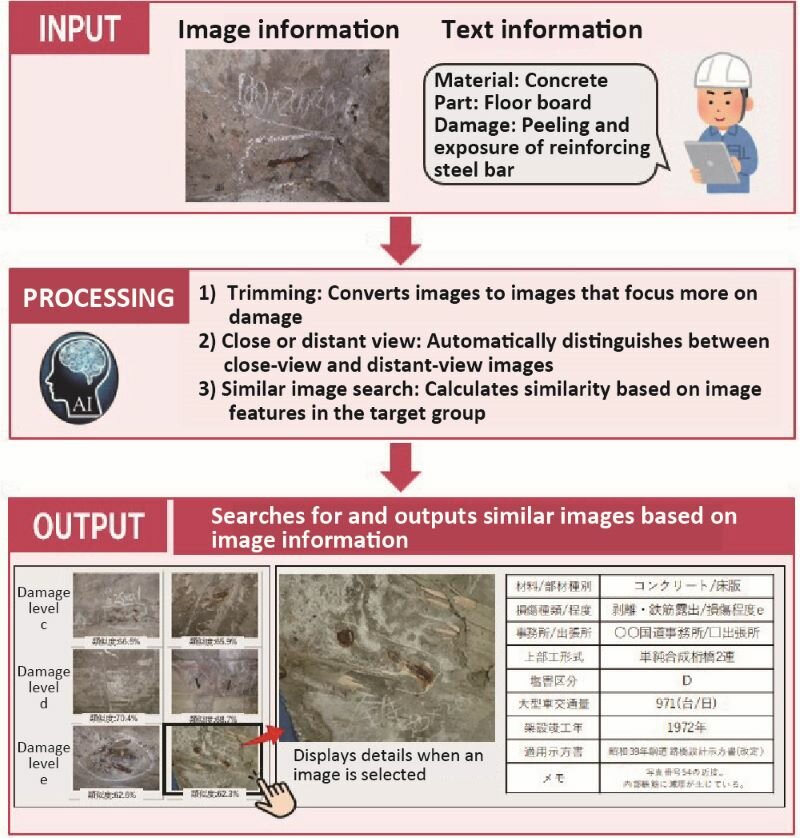
Image of processing by this system