- TOP
- Sustainability
- Risk Management
 Risk Management
Risk Management
1. Risk Management Basic Policy
(1) Basic Philosophy
The Group’s risk management approach, which includes crisis management, is defined by its risk management regulations as follows: “Identification and control of risks that could negatively impact our business operations before such risks materialize, with prompt action taken to minimize potential losses should a risk materialize.”
The Group operates based on five fundamental principles of corporate management: 1) enhancing corporate value, 2) preserving and effectively utilizing managerial resources, 3) ensuring sustainable and stable business continuity, 4) maintaining stakeholder trust while ensuring profitability, and 5) safeguarding the well-being of our employees and related parties. To achieve the above, we believe it is essential to accurately recognize risks and opportunities that warrant our attention. This involves implementing strategies to decrease the likelihood of risks occurring, along with preparing measures in advance to mitigate potential losses should these risks materialize. We also believe that taking decisive action to limit the impact on all involved parties during emergency situations is an essential aspect of risk management.
(2) Action Plan
To put this basic philosophy into practice in concrete terms, we have established a comprehensive risk management framework throughout the organization. We aim to actively and continuously advance risk management as a Group in accordance with the following action plan:
- ① We recognize the Group’s societal obligations and public mission, and we shall manage a variety of risks in a responsible manner to promote ethical and fair corporate activities.
- ② By providing education, training, and sharing information, we shall strive to cultivate each employee’s sensitivity to risk and enhance their risk response capabilities.
- ③ We shall encourage stakeholder engagement, forge trustful relationships with stakeholders, and ensure that our actions do not compromise their interests.
- ④ During emergencies, we shall act promptly and appropriately to limit damage to involved parties and undertake decisive action to bring about a rapid recovery.
- ⑤ In emergency situations, we shall prioritize the safety of our staff and related parties, and we shall strive to ensure the continuity of our operations wherever possible.
- ⑥ We shall aim for proactive and impartial disclosure of risk-related information and foster open communication with the broader society.
2. Risk Management System
To uphold its risk management principles, the Group has established a Risk Management Committee, chaired by the Representative Director and President, CEO, to promote appropriate risk management(Figure 1). The Risk Management Committee works in concert with the Sustainability Committee, annually formulating policies and strategies related to the Group’s risk management. In addition to identifying risks from a mid- to long-term perspective and evaluating the nature of said risks, the expected scenarios, the frequency of occurrence, and the extent of the damage, it also analyzes the impact on our business and operations, formulates response strategies based on these considerations, and keeps track of the status of individual risk management efforts while providing guidance and supervision. Moreover, it reports on the state of initiatives to the Board of Directors, which holds discussions about said initiatives, thus exercising oversight and control over all risk management activities.
![[ Figure 1: Risk Management System Diagram ]](/english/sustainability/risk-management/img/figure01.png)
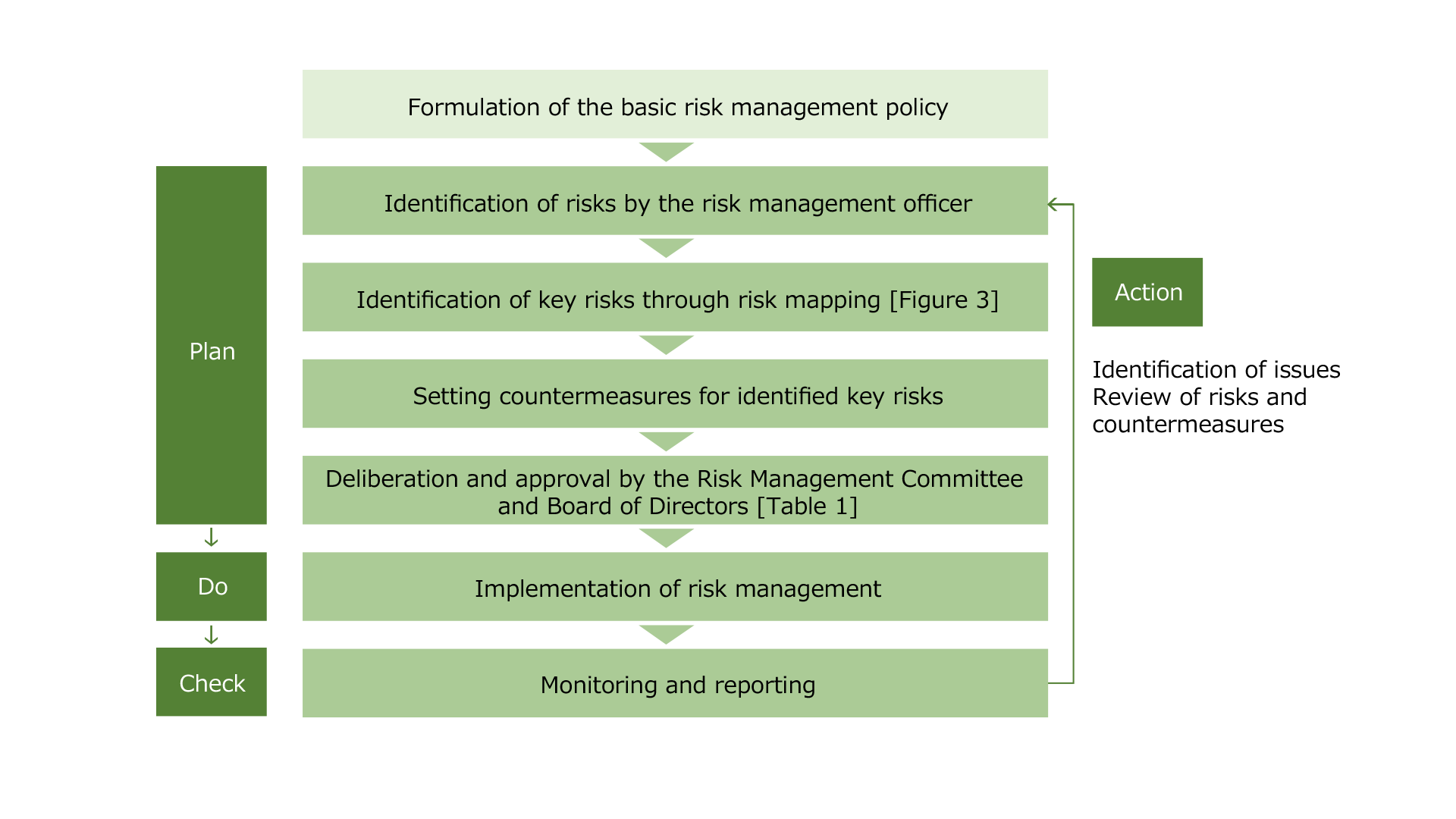
3. Identification of Key Risks and Countermeasures
In order to enhance the efficacy of risk management and build a relationship of trust with stakeholders, we have identified key risks that need to be specifically addressed by the CTI Engineering Group, and established countermeasures to reduce the impact of risk occurrence.
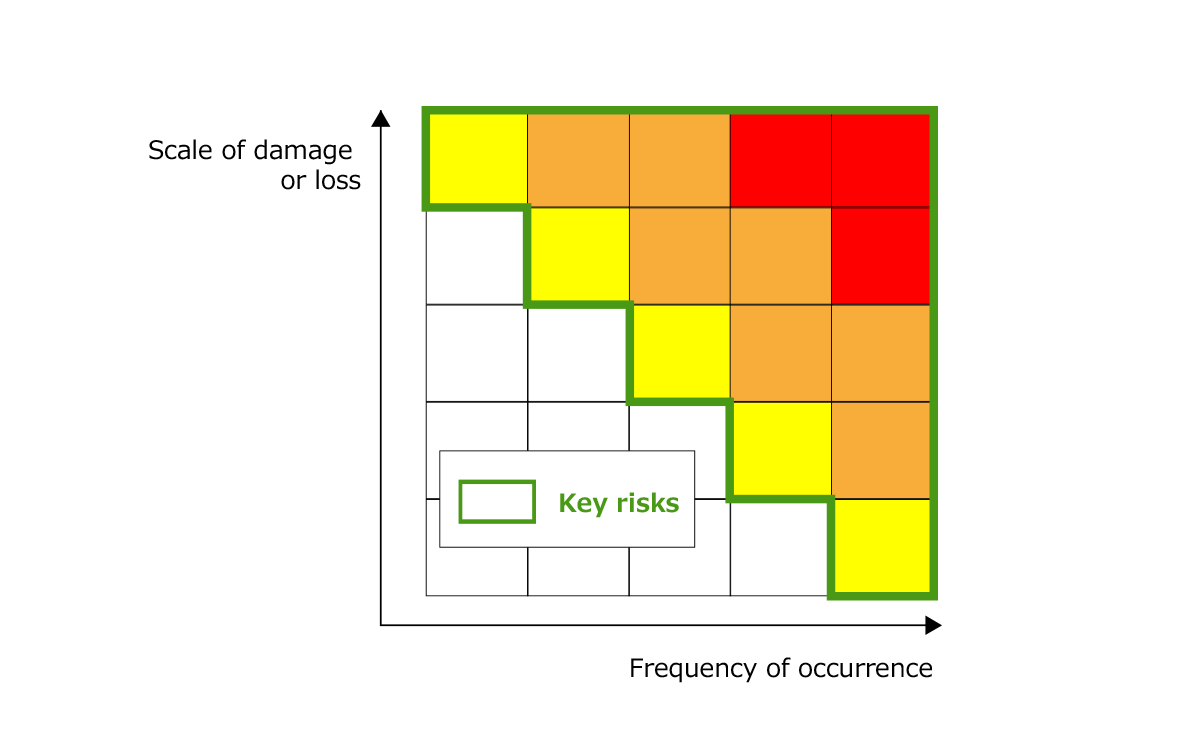
As shown in Figure 2, key risks are identified by the risk management officer as risks (not including opportunities) arising from external environmental changes or internal to the organization, according to the basic risk management policy. These identified risks are plotted on a risk map (Figure 3) according to the scale of damage or loss and frequency of occurrence to identify them as key risks, and various countermeasures are then formulated according to the content of the risks (Table 1). These decisions are confirmed after deliberation by the Risk Management Committee and approval by the Board of Directors. The identified key risks and countermeasures will be monitored, and reviewed as necessary through the PDCA cycle.
| Risk area | Key risks * | Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|
| Risks associated with changes in the external environment | ||
| Market | ・Excessive price competition ・Shrinking public works project budgets, market changes ・Major changes in the business environment due to technological innovation |
・Lower costs through DX progress ・Expansion into public-private partnerships, private markets, etc. ・Promote research and development in response to technological innovation and social changes ・Rapidly introduce innovative technologies |
| Standards, legal regulations | ・Enactment or revision of standards and laws that affect business activities (e.g., the Act for Promoting Proper Tendering and Contracting for Public Works, the Housing Quality Assurance Act, the Unfair Competition Prevention Act, the Civil Code, the Companies Act, the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, the Labor Standards Act, the Industrial Safety and Health Act, etc.) | ・Gather up-to-date information and respond promptly |
| Climate change, natural disasters, pandemics | ・Impact of natural disasters and infectious diseases on business ・Delayed response to climate change countermeasures |
・Prompt response and ongoing training for BCP ・Formulate BCPs for new infectious diseases ・Proactive response to projects related to climate change countermeasures ・Promote research and development to acquire related technologies |
| Investment | ・Losses from investments in corporate acquisitions, new businesses, etc. | ・Consider and ascertain the business environment ・Ongoing monitoring of investment projects |
| Securing and developing human resources | ・Declining competitive advantage due to delays in securing and training human resources and increased outflow of human resources from the company | ・Continue aggressive recruitment activities ・ Promote diverse work styles ・ Enhance various education and training programs |
| Information security | ・System failure or information leakage due to cyber attacks, etc. | ・Harden systems against cyber attacks ・Thorough information security education |
| Country risks | ・Political instability (war, revolution, civil disorder, terrorism), sudden changes in economic policies and conditions, currency fluctuations ・Impact of economic sanctions, etc. on business activities |
・Gather information on country risks ・Reinforced responses in the event of terrorism, etc. ・Disperse and expand countries and areas of operation |
| Risks originating within the organization | ||
| Quality and safety | ・Contract noncompliance ・Serious accidents due to inadequate safety management |
・Raise the level of the Quality Management System ・Thorough safety management training |
| Technical strengths | ・Decline in technological capabilities ・Insufficient adaptation to technological innovation due to stagnant R&D, etc. ・Decline in productivity |
・Promote technological enhancement ・Promote planned research and development ・Promote production system reforms |
| Personnel and labor | ・Loss of social credibility due to long working hours, human rights issues, mental health problems, and harassment | ・Promote measures through labor-management cooperation to prevent long working hours ・Thorough education on respect for human rights and prevention of harassment ・Raise employee engagement |
| Compliance | ・Accounting fraud, embezzlement and bribery, violation of antitrust laws, infringement of intellectual property rights, insider trading, and removal of confidential and personal information | ・Expand compliance training and education ・Thorough measures to prevent information from being taken out of the company ・Reinforce internal audit systems |
*Only risks are listed, not opportunities.